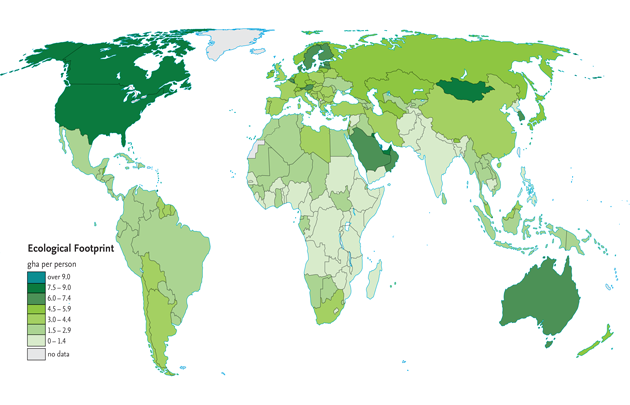
Ecological Footprint
The Ecological Footprint measures the area of biologically productive land and water required to produce the resources an individual or a population consumes and to absorb the waste it generates. A country's Ecological Footprint is usually expressed in global hectares (gha) per person - the average area of land required to support each of that country's inhabitants. Since 1961, when the data from which the Ecological Footprint is calculated first became available, there has been a marked increase in the contribution made by the carbon footprint - that is, the amount of forest land needed to absorb emissions of carbon dioxide (CO2). Most CO2 emissions come from the burning of fossil fuels.